
Excessive Sweating Can Be Managed
Sweating is a natural process of the human body. However, when it becomes excessive, it can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life.
In this article, we’ll explain the causes of excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) and how to manage it effectively. You’ll also find practical self-care tips to reduce sweat, control odor, and restore confidence.
Table of Content : Excessive Sweating
What Causes Excessive Sweating?
Excessive sweating occurs when the nerves that control sweat glands become overstimulated, leading to an abnormal increase in sweat production.
Several factors can trigger this condition, including the body’s metabolism, emotional responses, certain foods, and some underlying health conditions.
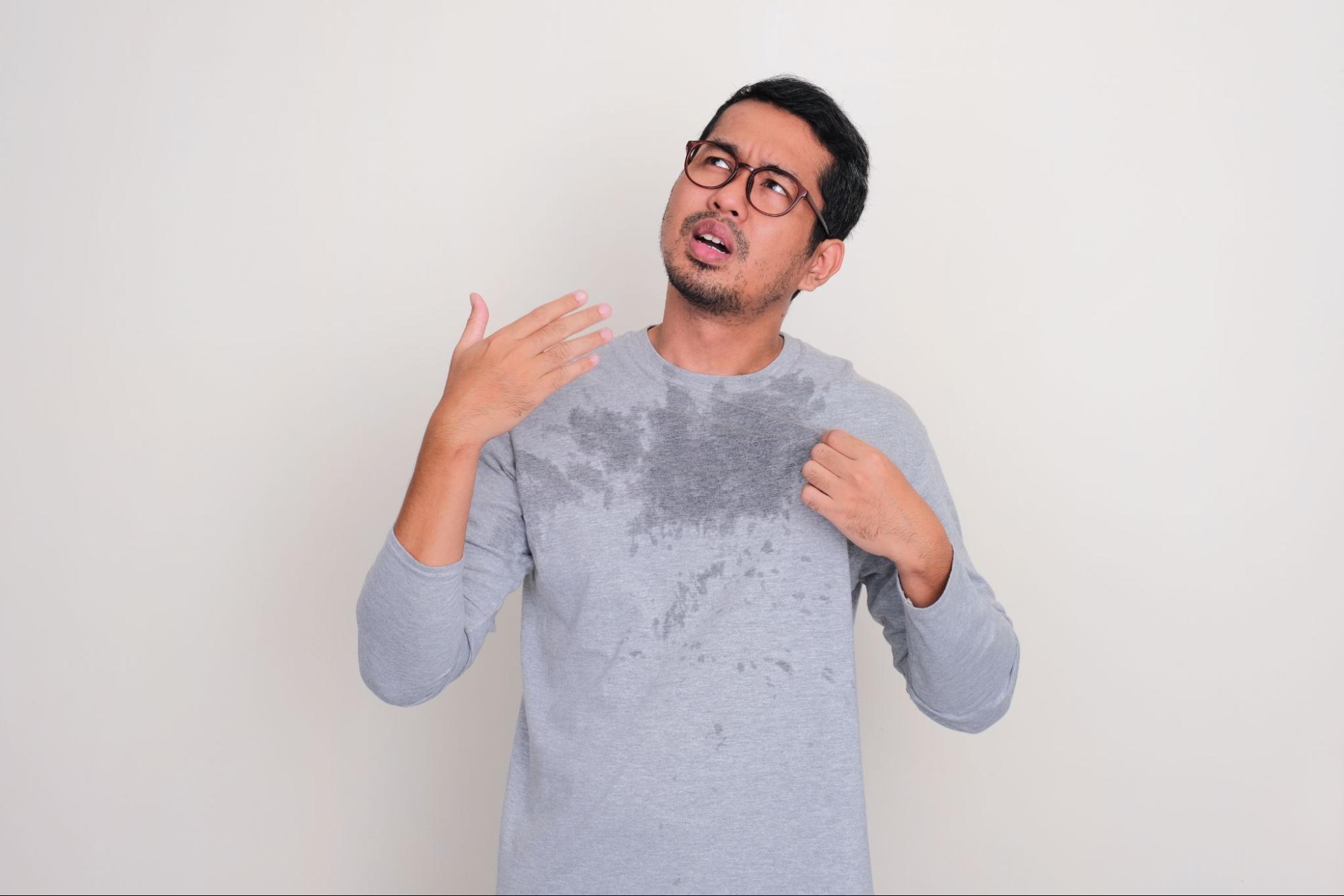

What Is Sweat and Why Does the Body Produce It?
Sweat is a fluid produced by sweat glands found throughout most of the skin, except in areas like the lips, nail beds, and certain mucous membranes. Sweat consists primarily of water (over 99%) along with electrolytes like sodium, chloride, potassium, and calcium. It also contains small amounts of waste substances such as urea and lactic acid.
Sweating is a normal physiological function and a sign that the body’s thermoregulation system is working properly — helping to release heat and maintain a stable body temperature.
How to Know If You’re Sweating Excessively or Not
The amount of sweat varies from person to person. You can start by observing your own symptoms to see whether your sweating pattern is normal or excessive:
- Sweating from heat or exercise → Normal.
- Sweating from stress, excitement, or anxiety → Normal. This is an emotional response naturally triggered by the body.
- Excessive sweating (Hyperhidrosis) → Abnormal. Sweating too much, even without heat or physical activity, or only in specific areas, may require medical consultation.
- Reduced or absent sweating (Anhidrosis) → Abnormal. When the body cannot sweat properly, it may lead to overheating or even heat stroke.
Normal sweating is healthy and essential for maintaining body temperature. However, if you notice that your sweating is excessive or unusually minimal, especially in hot environments, you should consider a health check to identify possible underlying causes.
Comparison Table: Normal vs. Abnormal Sweating
| Type of Sweating | Characteristics | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Normal sweating |
| Stay hydrated, replenish electrolytes, and maintain good skin hygiene |
| Abnormal sweating (Excessive) |
| Medical consultation may be needed. Treatment options include topical or oral medications, Botox injections, and laser therapy |
| Abnormal sweating (Reduced or none) |
| Risk of heat stroke. Rest in a cool area, drink water, and seek medical attention to determine the cause |
Causes of Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating can be categorized into two main types, based on underlying causes and characteristics:
- Primary Hyperhidrosis: Occurs without any identifiable medical cause, usually affecting specific areas such as the palms, soles, underarms, face, and groin. It often begins in childhood or adolescence and can persist throughout life. Triggers include emotional stress, heat, and physical activity.
- Secondary Hyperhidrosis: Caused by medical conditions or side effects of medications. Common factors include:
- Endocrine disorders (e.g., hyperthyroidism, diabetes)
- Neurological disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury)
- Infections (e.g., tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS)
- Cancer (e.g., lymphoma)
- Medications (e.g., antidepressants, antipsychotic drugs)
Common Areas Prone to Excessive Sweating
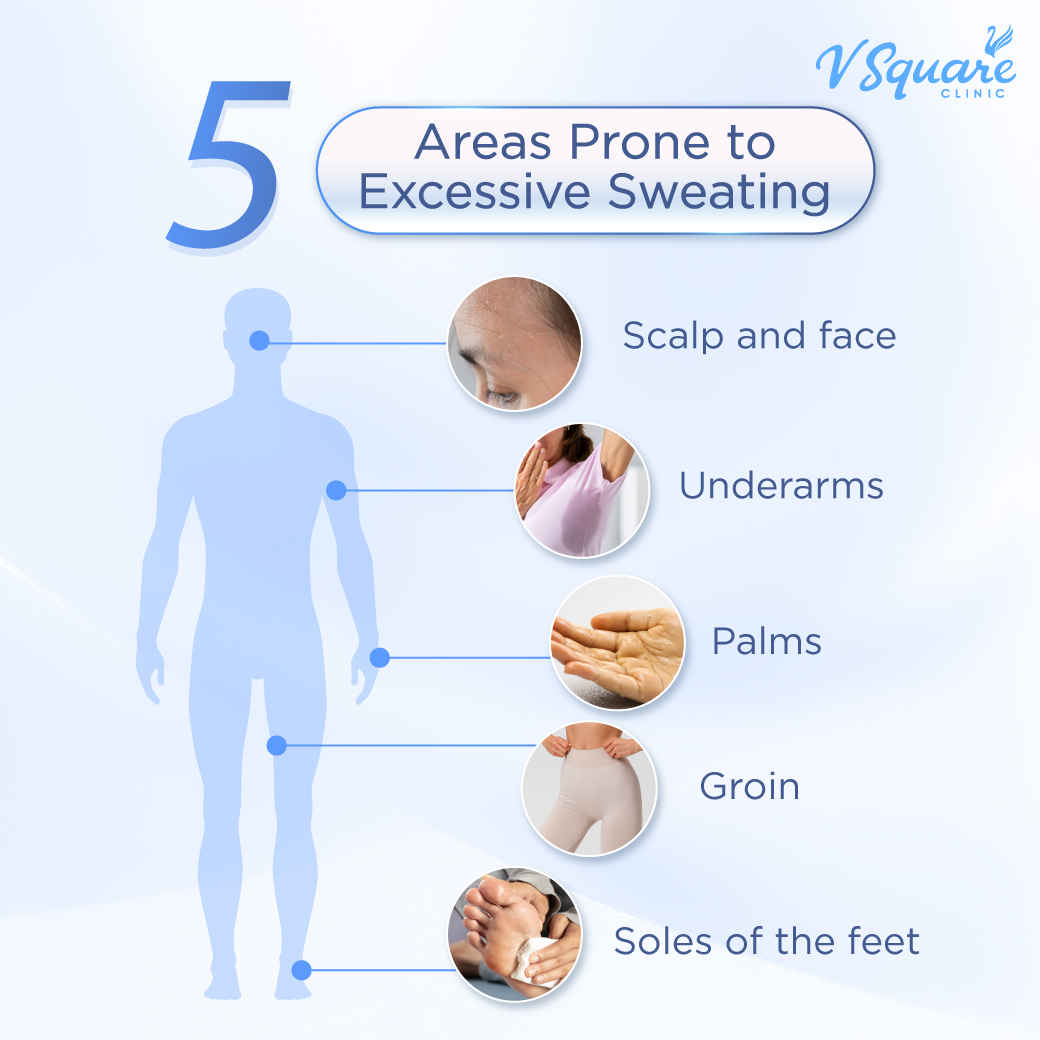
Sweat can be produced from almost every part of the body. However, certain areas contain a higher concentration of sweat glands and therefore tend to sweat more easily. These commonly include:
- Underarms
- Palms
- Soles of the feet
- Scalp and face
- Groin area
Is Excessive Sweating Abnormal?
Whether excessive sweating is considered abnormal depends on several factors — including the amount, duration, and underlying cause. In the previous section, we compared normal to excessive sweating. Here are some specific signs that may indicate abnormal sweating (Hyperhidrosis):
- Sweating so much that your hair or clothes become soaked, requiring multiple outfit changes per day
- Persistent sweating that lasts for several weeks or months
- Sweating excessively without an identifiable cause — such as in cool environments, without physical activity, or without consuming spicy foods or stimulants
Is Excessive Sweating Dangerous?
In most cases, excessive sweating isn’t dangerous or life-threatening. However, it can have a major impact on both physical comfort and emotional well-being, as shown below:
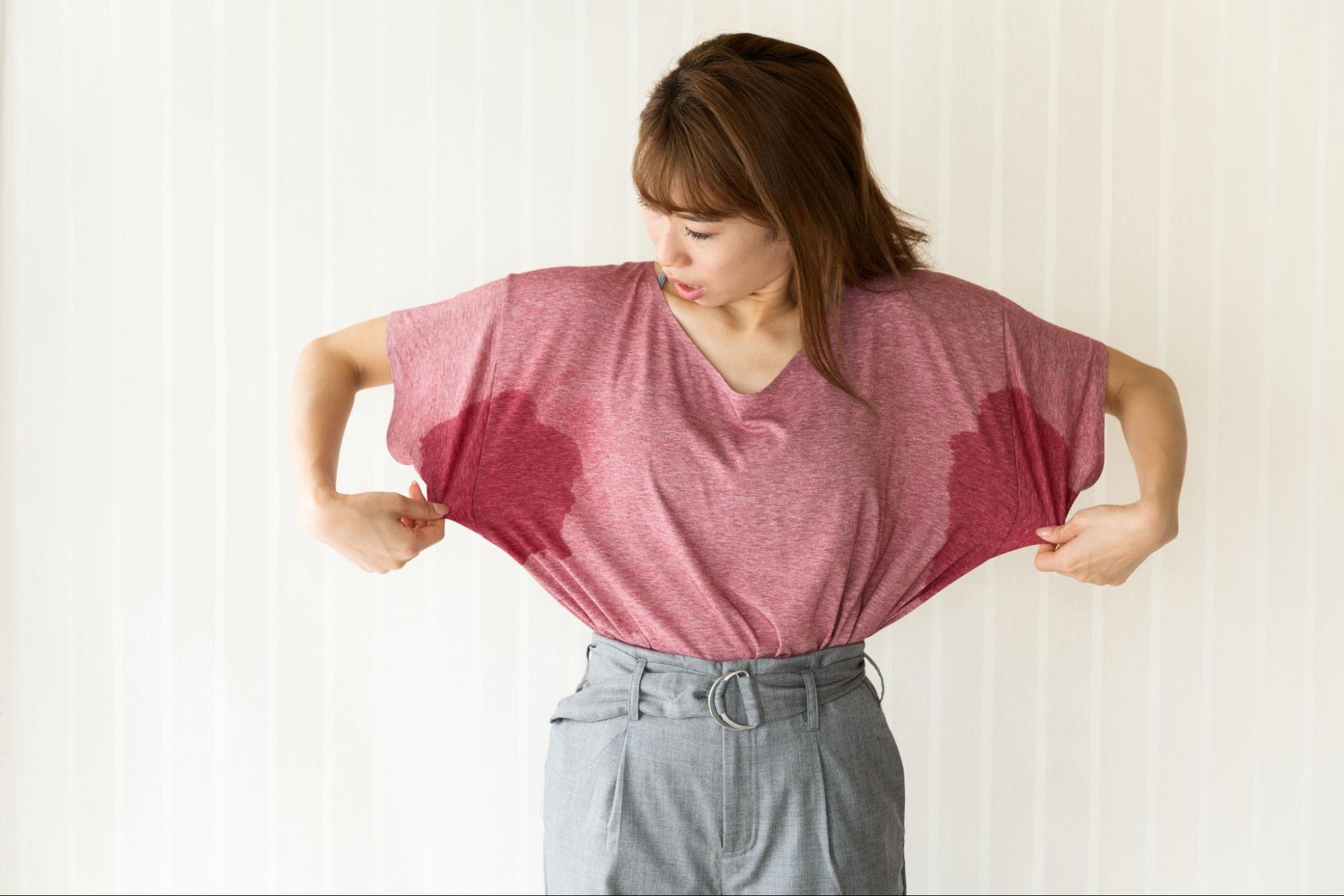

- Physical discomfort: Excessive sweating can make you feel unclean or uncomfortable — for example, needing to change clothes often or dealing with lingering body odor.
- Emotional distress: Excessive sweating may cause psychological discomfort such as stress, embarrassment, or loss of self-confidence, which can interfere with work and social interactions.
- Infection risk: Constant moisture can irritate the skin, leading to inflammation or bacterial and fungal infections.
That said, in some cases, abnormally excessive sweating may signal an underlying medical condition, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes, or certain cancers. If your symptoms are persistent or unexplained, it’s best to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How to Treat Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating can be effectively treated with medical procedures or medications performed under the supervision of a qualified doctor.
- Botox injections for sweating: Botox can be injected into areas such as the underarms, palms, or soles to temporarily block nerve signals that activate sweat glands, reducing sweat production.
- Topical or spray antiperspirants: Products containing aluminum chloride help decrease perspiration and control odor in patients with hyperhidrosis.
- Oral medication: Certain medications, such as glycopyrrolate, can reduce stimulation of the sweat glands and lower sweat production.
- Surgical treatment: In severe or resistant cases, surgery may be considered to cut or remove overactive sweat glands.
- Underarm laser treatment: Since underarm hair can trap sweat and bacteria, laser hair removal can help reduce dampness and odor in this area.
How to Manage Excessive Sweating at Home
Proper self-care and daily hygiene can help control excessive sweating and improve comfort. Making small lifestyle changes and choosing the right personal care products can make a noticeable difference.
- Wear breathable clothing: Choose natural fabrics like cotton or linen to improve airflow and help keep the body cool.
- Take cool showers: Cold showers help lower body temperature and temporarily reduce sweat production.
- Use alum (potassium alum): A natural mineral that can be applied to sweat-prone areas such as the underarms or palms to minimize perspiration.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water helps maintain hydration, reducing the body’s need to release excess heat through sweat.
- Avoid spicy foods and alcohol: Both can stimulate the body’s temperature regulation system and increase sweating.
- Manage stress and emotions: Emotional triggers like anger, fear, or anxiety can overactivate sweat glands; relaxation techniques can help.
- Consult a doctor if symptoms are severe: If sweating is excessive, unexplained, or persistent, seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and safe, effective treatment.
How to Manage Excessive Sweating with Body Odor
People who sweat excessively — especially in the underarm area — often experience body odor that affects their confidence and daily life. Here are several effective treatments we recommend to reduce both sweating and odor:
1. Botox Injections for Sweat Reduction
Botox for sweating involves injecting botulinum toxin type A into areas with excessive sweat production — such as the palms, soles, or underarms. This temporarily blocks the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, thereby reducing sweat production.
Besides controlling sweat, Botox also helps limit bacterial buildup, which reduces body odor and improves overall comfort.
2. Underarm Laser Hair Removal
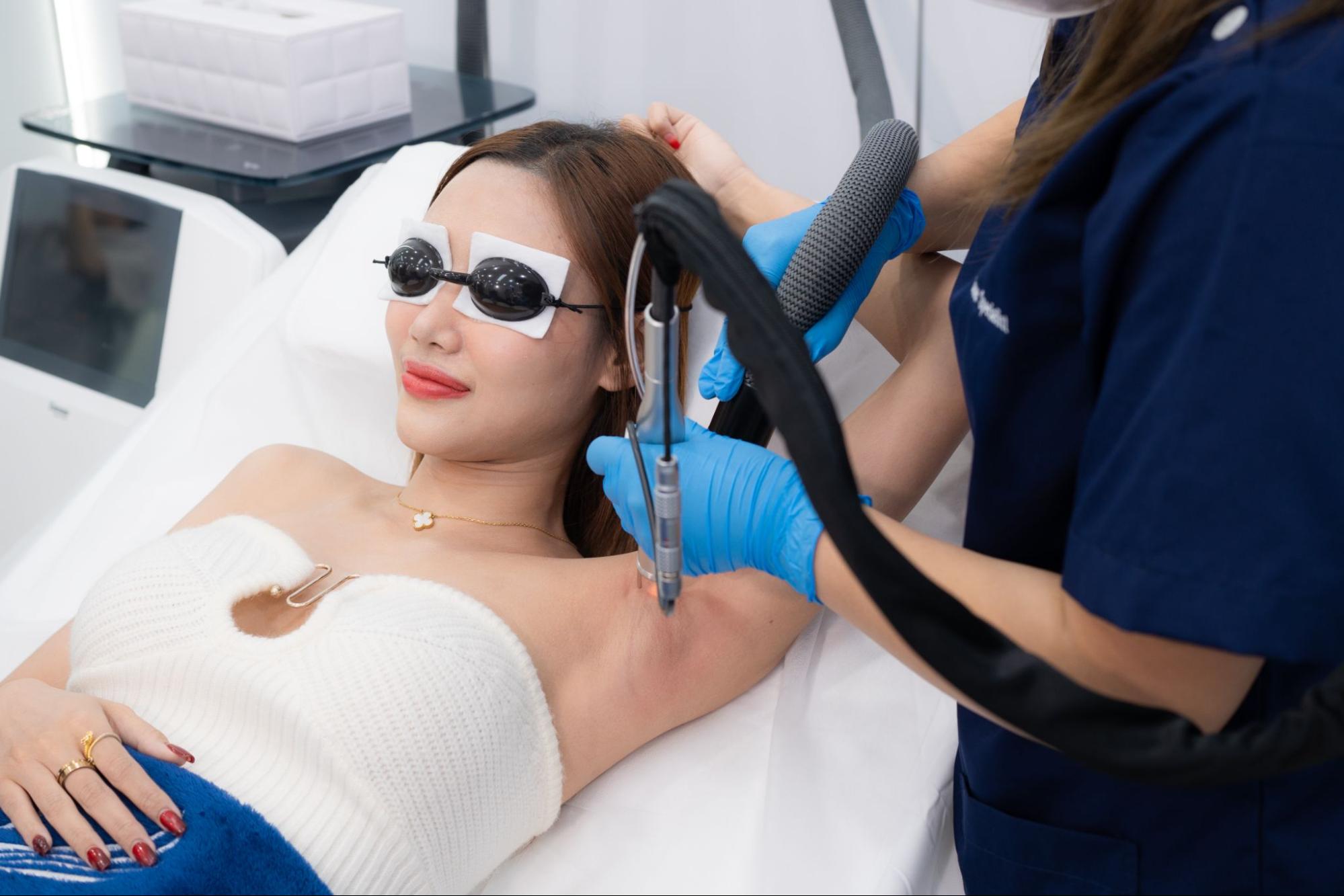
Laser hair removal works by destroying hair follicles in the underarm area using focused laser energy. Although it doesn’t directly stop sweating, it helps reduce odor and underarm dampness because armpit hair traps sweat and bacteria. An added benefit is that laser treatment can lighten dark underarms and leave the skin smooth, clean, and odor-free.
3. Laser Sweat Gland Destruction
Laser or thermal energy treatments — such as Microwave Thermolysis — can permanently destroy sweat and odor glands in the underarm area. This method is suitable for people with severe hyperhidrosis, offering long-lasting results in reducing both sweat and odor.
However, it is more expensive and may cause mild swelling, bruising, or temporary numbness after the procedure.
4. Surgical Removal of Sweat Glands
Surgical procedures can be performed in several ways, such as removing sweat glands under the arm or cutting the nerves that control sweating (Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy – ETS).
While surgery can provide long-term results, it carries potential risks including scarring, complications, or compensatory sweating (increased sweating in other parts of the body).
5. Topical Antiperspirants
Antiperspirant creams or sprays containing high concentrations of aluminum chloride are often recommended for mild cases. They can be applied to areas like the underarms, palms, or soles.
These products are affordable, easy to use, and readily available, though some individuals may experience skin irritation, itching, or redness, making long-term use difficult.
6. Oral Medication to Reduce Sweat Gland Activity
Anticholinergic drugs such as glycopyrrolate or oxybutynin work by inhibiting the activity of sweat glands throughout the body. They are suitable for individuals with generalized sweating but may cause side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, heart palpitations, or difficulty urinating. These medications should only be taken under medical supervision.
7. Iontophoresis Therapy
Iontophoresis uses a mild electrical current passed through water to temporarily block sweat gland activity in the hands or feet. It is a non-surgical treatment suitable for people with excessive sweating on palms and soles.
However, it requires multiple sessions for visible results and must be performed regularly, which may be inconvenient for those with limited time.

For a safe, effective, and no-downtime option, Botox injections can precisely reduce excessive sweating with long-lasting results. Underarm laser hair removal doesn’t stop sweating but helps remove hair, reduce bacteria, and minimize odor for cleaner, fresher underarms.
Interested in Botox for sweat reduction or underarm laser hair removal at V Square
Clinic? Click to check the latest promotions.

FAQ — Common Questions About How to Treat Excessive Sweating
What’s the difference between Botox and laser hair removal for underarm sweating?
Botox injections directly target sweat glands to reduce perspiration and deliver visible results — ideal for those with excessive sweating.
Meanwhile, underarm laser hair removal focuses on removing hair and reducing odor, but it does not stop sweat production.
How soon will I see results after Botox for sweating?
You’ll begin to notice reduced sweating within 3–7 days after treatment. In some cases, especially in hot weather, sweat production may temporarily increase before it stabilizes.
How long do the results of Botox for excessive sweating last?
The effects typically last about 3–5 months per session. To maintain results, repeat treatments can be performed as advised by your doctor.
How many units of Botox are needed to treat excessive sweating?
The amount of Botox needed depends on the size and area being treated. On average, 50–100 units per side (around 20–30 injection points) are typically used for underarm treatment.
Which is better — Botox or underarm laser hair removal?
Botox injections are a more precise solution for reducing sweat. However, combining both treatments can enhance results — controlling sweat while also minimizing odor and leaving the underarms cleaner and smoother.
Summary — Safe and Effective Ways to Treat Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating that interferes with daily life — especially in areas such as the underarms, palms, or soles — can affect confidence and personal comfort. Botox injections are an effective, safe option that directly targets sweat glands, reduces perspiration, and delivers fast, long-lasting results.
For those interested in Botox for sweat reduction, feel free to contact V Square Clinic via inbox for a personalized consultation. Our experienced doctors will evaluate each case individually to determine the right Botox brand and dosage for the best results.
When sweating decreases and the underarms become smoother and hair-free, you’ll feel fresher, cleaner, and more confident in any situation.
Reference
- Medicine (Baltimore). 2026 Jul 1;102(Suppl):e32764. doi:
10.1097/MD.0000000000032764 - J Lasers Med Sci. 2026 Dec 29;14:e71. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2026.71

สำหรับผู้อ่านทุกท่านที่มีข้อสงสัยเพิ่มเติม ทีมแพทย์ V Square Clinic ทุกคนยินดีให้คำปรึกษาฟรี โดยไม่มีค่าใช้จ่าย หรือสามารถปรึกษาหมอทาง inbox facebook หรือ Line นี้ได้เลยครับ หมอตอบเองครับ





